Norfolk once boasted many major airfields, virtually all of which are now closed to military flying. Marham is the only major survivor spearheading the RAF’s front line fighter force, in conjunction with Lincolnshire’s RAF Coningsby and RAF Lossiemouth in Moray, Scotland.
However, during the Second World War the Norfolk landscape was very different; it was littered with front line airfields, composed mainly of light bomber and fighter squadrons, all of which could be found with relative ease.
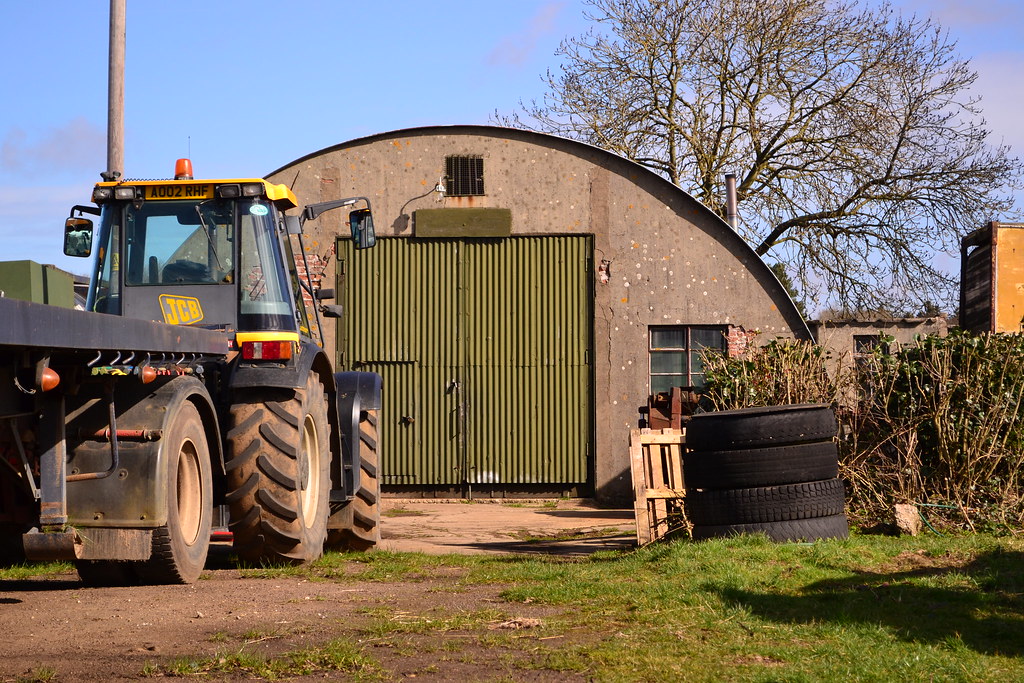
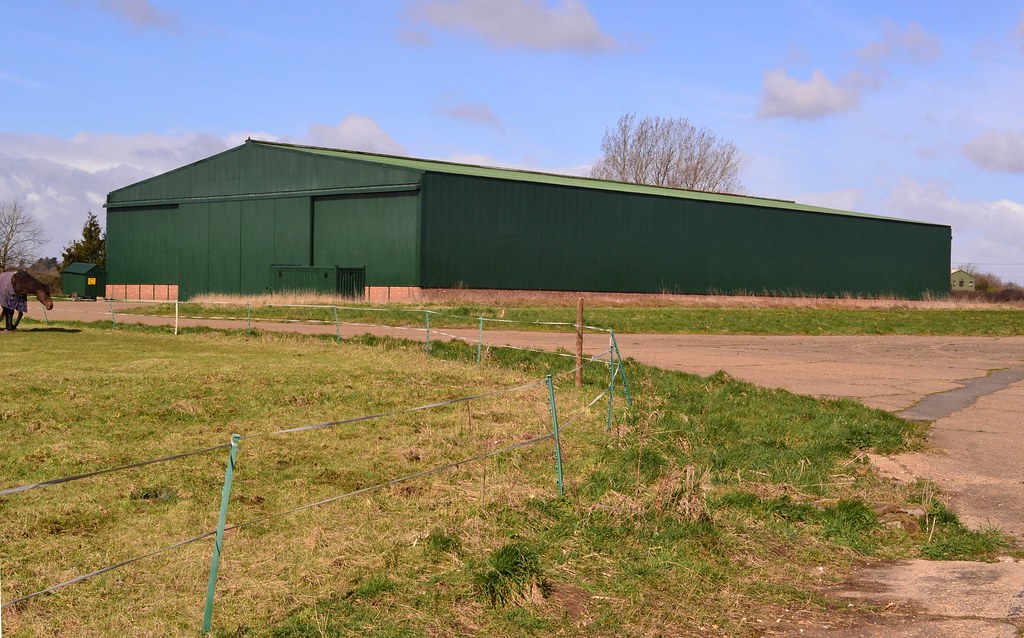
One such airfield was that of Watton. Used by a range of light and heavy aircraft, its history was chequered, bearing witness to some of the more gruesome aspects of the air-war.
Today it is a housing estate, the single runway remains and is used for storage, the hangers and technical buildings have gone and the accommodation areas have all been sold off. That said, the perimeter track remains in part, the ‘feel’ of the airfield hangs over the area and a number of memorials pay silent tribute to those who served here.
Found on the edge of the town of Watton in Norfolk, we go back to this once busy RAF base and see what has changed, and relive the life of RAF Watton.
RAF Watton (Station 376)
RAF Watton, located some 11.5 miles north-east of Thetford, opened in 1939 as a medium bomber station with the RAF. Unusually it only had one runway, a grass example, which was later extended to 2,000 yards and crossed the airfield in an east-west direction.
The late 1930s saw a massive expansion of Britain’s military might, and in particular, its airfields. With little foresight into what lay ahead, these pre-war and early war airfields were not designed, nor built, as dispersed sites. Once the realisation of what the war would bring hit home however, later examples would be dispersed, giving a new dimension to airfield design. As a result, Watton (built by the John Laing company) was constructed with much of the accommodation block, technical area, hangars and so on, all being placed closely together on one single site.
Housing for the personnel was located in the north-western corner, with the technical area just east of this. The bomb dump, an ideal target, was further to the east of this area. Four ‘C’ type hangers were constructed each having a span of 150 feet, a length of 300 feet and a height of 35 feet. Whilst Watton was a medium bomber airfield, and thus aircraft were relatively small, it was envisaged at this time that larger, heavier bombers would soon come on line, and so foresight deemed larger than necessary hangar space be provided. A 1934/35 design, these hangars would be common place across expansion period airfields.
Another architectural design found at Watton was the redesigned Watch Office, an all concrete affair built to drawing 207/36, it was one that would very quickly become inadequate, requiring either heavily modifying or, as was in many other cases, replacing altogether.
Partially opened in 1937, the airfield wasn’t fully completed and handed over to the RAF until 1939. Being a pre-war design, building materials were in good supply, and so the accommodation blocks were constructed using brick, and they catered well for those who would find themselves posted here.
Another aspect considered at this time was that of camouflage; airfields were enormous open expanses and could be easily seen from great distances and heights. Numerous proposals for hiding them were put forward, a move that resulted in the formation of a special unit within the Directorate of Works led by Colonel Sir John Turner. Watton came under the eyes of Sir John and his department, and this led to an ingenious camouflage pattern of fields and hedges being painted across the entire airfield, thus disguising it from prying eyes above. Whilst not completely effective, it certainly went some way to protecting it from attack.

Watton airfield taken in 1942 by No. 8 Operational Training Unit. The four hangars can be seen in the centre of the photo with the patchwork of ‘fields’ disguising the main airfield. English Heritage (RAF Photography).
The first postings to arrive were the men and machines of 21 and 34 Squadrons RAF. Their arrivals on March 2nd 1939 saw a reuniting of both squadrons under the Command of Group Captain P. J. Vincent DFC and 6 (B) Group . On the 7th, the airfield was inspected by the Group’s AOC after which 34 Sqn performed a flypast; one such event that would be the start of many visits from numerous dignitaries including the Marshall of the Royal Air Force himself, Sir Edward Ellington GCB, CMG, CBE.
Little flying took place by either squadron at this time however, as the aerodrome was soon unserviceable due to the very poor British weather. Grass runways soon became bogs, and as was found across many grassed airfields at this time, unsafe for aircraft to either take off or land without mishap. From April things picked up slightly, and intensive training began in the form of station tactics and defence exercises. The weather would however, continue to be the worst enemy, repeatedly preventing or restricting flying from taking place.
In August, 34 Sqn received orders to depart Watton and proceed to Singapore, and so on the 12th, the air and ground parties began their long transit leaving Watton and England far behind. The quiet of their departure would not last ling however, as within a few days of them leaving, their empty beds would be filled once more, when the Blenheims and crews of 82 Sqn arrived.
At 11:05 on September 3rd 1939, notification came though to Watton of Britain’s declaration of war. Within days of the announcement aircraft were being moved out under the ‘Scatter’ scheme to another airfield, Sealand, for there was a fear of imminent air attacks following the war’s declaration. The Blenheims remained at Sealand until mid September, at which point they were recalled and prepared for attacks on vessels belonging to the German Navy. These vessels were not located however, and so the order to stand by was cancelled and the crews stood down. This would sadly become a regular and frustrating occurrence for the men of 21 Sqn.
Shortly after on the 9th, the first of the new MK.IV Blenheims were collected from Rootes Ltd at Speke, with further examples arriving over the next few days. Further movements saw aircraft detached to Netheravon and then onto Bassingbourne where Blenheim L8473 was damaged as it ‘nosed over’ whilst taxiing. A minor, but unfortunate accident, it would be the first of many more serious losses for the squadron.
On 26th September, another order came through for aircraft of 21 Sqn to stand by to attack the German fleet, whilst a further two Blenheims (L8734 and L8743) would fly to the Rhur to carry out a photographic reconnaissance mission. However, bad weather, industrial smoke and a faulty camera prevented both aircraft from carrying out their duties: each one returning to Watton empty handed but unscathed – crews reporting heavy flak over the target area. The whole of October and November were pretty much a wash-out. Bad weather with prolonged heavy rain prevented any substantial flying beyond the local area. Air gunnery and co-operation flights were carried out whenever possible, but the late months of 1939 had certainly been a ‘phoney war’ for 21 Sqn.
As 1940 dawned, things on the continent began to heat up and ground attacks increased for both Watton squadrons. Low-level sorties saw them attacking troop formations and enemy hardware as its galloped its was across the low-countries. Whilst bravely flying on and escorted by fighters, overall loses for the slower Blenheims of 2 Group were beginning to rise, a pattern that would only increase in the face of a far superior enemy in the coming months.
These losses were borne out by 82 Sqn in dramatic style on the 17th May, when twelve aircraft took off at 04:50 to attack Gembloux. They were met with heavy anti-aircraft fire and overwhelming fighter opposition – fifteen BF.109s, decimated the squadron. All but one aircraft was lost, the only survivor being P8858 crewed by Sgt. Morrison, Sgt. Carbutt and AC Cleary. Whilst not injured in the melee, the aircraft was badly damaged and as a result, was deemed irreparable and written off. An entire squadron had all but been wiped out in one fell swoop.
This disaster would be reflected right across 2 Group, who had now suffered its greatest overall loss to date, but for 82 Sqn it would not yet be the end of this traumatic and devastating period. The burning cauldron that was now facing the light bomber was taking its toll on crews, who were all at a distinct disadvantage to their Luftwaffe counterparts. On the 21st, three more aircraft were lost from Watton, with one being forced down in France, another lost without trace and a third limping home so badly damaged it also had to be written off.
A short visit by 18 Sqn between 21st and 26th May barely interrupted proceedings at Watton. After returning from France, they had spent no less than nine days in May at five different airfields including the nearby Great Massingham.
By early June 1940 Operation Dynamo had been completed and France was lost. The British Bulldog, whilst not a spent force, had shown her teeth, been bitten hard and was now licking her heavy wounds. Preparations would now begin to protect her own shores from the impending invasion.
Fuelled by revenge, combined attacks by both 21 and 82 Sqn continued on into the summer months. But revenge alone does not protect a crew from superior fighters and heavy flak. On June 11th, three more 21 Sqn aircraft were lost whilst attacking positions around La Mare, it is thought all three fell to Luftwaffe fighters. Two days later on the 13th, another five aircraft were lost, two from 21 Sqn and three from 82 Sqn; losses were mounting for the light bombers and Watton was amongst those bearing the brunt of these. On the 24th, 21 Sqn saw a reprieve, whether to rest crews, take on a new role or simply regroup, they began a move north to RAF Lossiemouth in Scotland. 82 Sqn however, would remain at Watton, where they would carry on with the punishing raids over the continent.
After the arrival and departure of another short stay unit, 105 Sqn between 10th July and 31st October, Watton was now left in the lone hands of 82 Sqn, a situation that would remain until the spring of 1942.
The dramatic loss of eleven crews back in May would come back to haunt 82 Sqn in August that year. On the 12th, another twelve aircraft took off on a high altitude bombing mission to Aalborg in Denmark. The airfield they were to target was well defended, and as if history were to repeat itself, once again eleven of the twelve aircraft were lost. The only one to return, that of R3915 crewed by Sgt. Baron, Sgt. Mason and Sgt, Marriott, turned back early due to low fuel.
In the space of three months, an entire squadron has been all but wiped out not once, but twice, unsustainable losses that would surely bring the squadron to its knees.

Memorial to the crews lost at Aalborg, 13th August 1940. The propeller of Blenheim R3800, that crashed that day.
It was loses like this that helped convince the authorities to eventually withdraw Blenheims from front line service during 1942 – the Blenheim being long outdated and outclassed. At this time, Watton’s 82 Sqn, would begin their transfer to the Far East, a place they would remain at until the war’s end.
A lull in operations meant that Watton was then reduced to mainly training flights, through the Advanced Flying Unit. Small single and twin-engined aircraft providing the activity over the Norfolk countryside. Many of the crews being trained here would be shipped out to the satellite airfield at Bodney, before returning here for their evening meals.
A brief interlude in the May of 1942 saw the rebirth of the former 90 Squadron, a First World War unit that had gone through this very process on a number of occasions since its inception in 1917.
Flying the American B-17 ‘Flying Fortress’ or Fortress I as it was in RAF designations, 90 Sqn was set up to trial the use of the four-engined heavy for its suitability as an RAF bomber. During the first 15 days at Watton, the squadron gained personnel and received their first aircraft, after which they moved to nearby RAF West Raynham. Here they would begin these trials which also required the use of a number of smaller airfields in the local area. These included both RAF Great Massingham and RAF Bodney, neither of which were particularly suited to the heavy bombers.
Watton then saw no further operational units, and in the mid 1943, it was handed over to the Americans who began to develop the airfield into something more suitable for their needs. It was now that Watton would take on a more sinister role.
In Part 2 we see how the Americans developed Watton, and how it became two sites rather than just one, and also, how its role in Electronic countermeasure took it into the post war years.
The full story of Watton can be found in Trail 9.