Lincolnshire is understandably known as ‘Bomber County’. Airfields once littered this part of the world, and many have now gone, returned to agriculture, used for housing developments or industrial sites. The names of those who served there linger in street names, Spitfire Way, Lancaster Ave etc. In some respects, it brings me closer to my father’s experiences as he was based in this county at the end of his service. He talked fondly of Lincoln and stations such as RAF Manby. His memory, a little jaded as he came toward the end of his life.
So our first trip around the area included places both old and new. It will include an active airfield, three former airfields and three museums. A busy couple of days out but remarkable ones. Driving north through the Lincolnshire Fens, we head toward RAF Coningsby, one of the few active fighter airfields left.
RAF Coningsby.
As an active airfield I won’t dwell on too much, RAF Coningsby is a large open expanse with excellent viewing facilities located in a number of places around its perimeter. It is nestled on the edge of the village where extensive RAF housing can be seen. The designated viewing area is at the end of the runway and offers a great opportunity for photos and plane spotting. There seems to be a hardened crew of enthusiast permanently perched here with enormous telephoto lenses. A short distance toward the village finds the BBMF museum with its well stocked shop, super little museum and of course tours through the hanger of the famous BBMF.
Taking yourself back, round the airfield, diverting to a closed crash gate, you can see a BAC Lightning perched in one corner. Match this with the Phantom that was at the main gate and you have a good idea of previous residents of the airfield. Moving on to the other end of the runway, will place you nicely for photographing approaching aircraft as they come over the road, gear down and at a speed slow enough to get a half decent picture from.
Coningsby often sees visiting aircraft from overseas. In July 2015, after my initial visit, four Indian Airforce Sukhoi Su-30 MKI “Flankers” arrived for a two-week long operation in conjunction with the RAF Typhoons from Coningsby. A good opportunity to see Russian designed aircraft in the Skies over Britain. They brought with them a C-130 Hercules and C-17 Globemaster. More excellent photo opportunities for the enthusiast. Additional photos are on Flickr and a detailed write-up can be found on Tony Wilkin’s ‘Defence of the Realm’.
Being active, events and buildings can change overtime or even daily, its always worth stopping off at if you are in the area, On a good day, you may get to see the Typhoon display team, practice sessions or the BBMF running up their aircraft. A sight to behold. Come to Coningsby, on a warm day, have sandwiches and a camera and set yourself up for superb viewing and great day out.
Leaving Coningsby, head west toward the old RAF Woodhall Spa airfield a few miles up the road, to the north, and a stark difference.
RAF Woodhall Spa
RAF Woodhall Spa was originally built as a satellite to RAF Coningsby a short distance away, and opened on 1st February 1942. It was built with three concrete runways; two of 1,400 yds (1,353 m) and a third and main runway of 2,000yds all 50yds (46 m) wide. The site like other Standard ‘A’ class airfields had two T2 hangars and one B1, thirty-six pan-style hardstands and numerous support buildings scattered around its perimeter. Accommodation was spread over 7 sites, along with a WAAF, sick quarters and 2 communal sites all located to the south-east. The technical and administrative sites were also to the south-east side of the airfield between the accommodation areas and the main airfield.
A bomb store was well to the north and the main entrance to the north-west. A range of accommodation and technical style huts were used, Laing / Nissen / Seco and a Watch Tower to drawing 15956/40.

An aerial photograph of Woodhall Spa taken post war. The B1 and T2 hangers can be seen to the north-west, a further T2 to the south. The accommodation block are below the frame. (Copy of a photo at the Thorpe Camp museum).
One remarkable features of Woodhall Spa was the installation of six arrester gear units on the runways. These were designed to prevent aircraft overshooting the runway and were installed during the building programme. Some 120 units were manufactured in all but only a handful of sites had them. On October 22nd 1942, the Woodhall Spa units were tested using an Avro Manchester from the Royal Aircraft Establishment and all went well. However, as the war progressed, reservations were registered about such a technique and the units were never used ‘operationally’ in any of the allocated sites.
At the same time that Woodhall Spa opened, the newly equipped Lancaster (Mk I & III) squadron, 97 Sqn, moved from RAF Coningsby into RAF Woodhall Spa and within a month were flying operations from their new home. However, their first operation, mine laying, was to be fatal for three aircraft, cashing on the journey home. This was not to be the general theme for 97 Sqn though. For the next year they would prove themselves more than capable, hitting many targets accurately with bravery and courage.

Lancaster Mk I ‘R5495’ OF-N of 97 Sqn Woodhall Spa, bombs up. This aircraft was shot down over Essen 8th/9th June 1942, the crew were all killed.*1
The following March (1943) the main bulk of 97 Sqn moved to Bourn to form part of the new Pathfinder force, with detachments at Graveley, Gransden Lodge, Oakington and a further section remaining at Woodhall. On April 18th 1943, 619 Sqn was formed from the Woodhall Spa detachment retaining their Lancaster Is and IIIs. However, their stay was very short; they moved out to Coningsby in January 1944 and were replaced overnight by the famous 617 (Dambusters) Sqn.
During their year here, 619 Sqn would prove themselves further in raids over the Ruhr, Düsseldorf, Oberhausen and Krefeld. Casualties were light during these early missions, but in the following August (1943) the RAF a mounted a massive raid consisting of 596 aircraft on the V2 rocket site at Peenemunde. Three of the twelve aircraft sent by 619 Sqn would fail to return.
When 619 Sqn moved out, 617 Sqn moved in. Lead by Group Captain Leonard Cheshire, 617 Sqn were the elite of 5 Group, Bomber Command and accordingly were to be assigned some of the most difficult and outright dangerous precision bombing missions.
Throughout 1944, 617 Sqn would have many near misses, and losses, ranging from low-level bird strikes to fighter attacks and flak. Targets varied considerably including those at: Limoge (aircraft engine factory), the Antheor Viaduct, Albert, St. Etienne and Metz (aircraft parts factories); many using the new ‘Tall Boy’ 12,000lb bomb.
On 15th April 1944, 617 Squadron were joined by 627 Sqn and obtained some D.H. Mosquito VIs, using these to good effect in the Pathfinder role while their Lancasters continued with the bombing. In June, they had a small respite from bombing missions and on the day of the Allied Invasion, they were tasked with dropping ‘Window’ over the Pas-de-Calais to fool the Germans into believing the invasion force would strike there.
Throughout the remainder of 1944, 617 Sqn continued to use ‘conventional’ and Tall Boy bombs on prestige targets like U-boat pens and the Samur Tunnel. Cheshire found himself handed a P-51, and after having it unpacked and engine tested, he used it to mark a V1 target to which 617 struck a devastating blow.
Further major targets were to befall the wrath of 617 Sqn. Flying 2,100 miles to a forward operating base at Yagodonik with Lancasters from 9 Sqn, they attacked the German main Battleship the ‘Tirpitz’. During the mission, for which they had long-range fuel tanks, of the 38 aircraft that set off, six were to crash on the outward journey, one turn back and one to crash on the return. The Tirpitz however was to remain ‘unsinkable’ for some time. It would take two more return trips by 617 Sqn from Lossiemouth to finally sink the ship, the last being on 12th November 1944, with the loss of 1000 German sailors.
Bombing and pathfinder operations for Woodhall spa crews continued right up to the end of the war. Early that year they would start to use the new ‘Grand Slam’ 22,000lb bomb, with their last operational fatality being on 16th April 1945. That was not the end for Woodhall Spa though. The famous Guy Gibson drove here and ‘borrowed’ a Mosquito of 627 Sqn against a backdrop of changed minds, mishaps and misjudgements, the resulting crash leaving him dead.
Woodhall closed soon after the war ended, but it was identified as a suitable location for Britain’s air defence missile the ‘Bloodhound’ and on May 1st 1960, Woodhall Spa became the base of 222 Sqn with Bloodhound MkI missiles. These were disbanded in June 1964 and replaced by Bloodhound Mk IIs of 112 Sqn on November 2nd 1964. These stayed until 1st October 1967 when they moved to Episkopi in Cyprus.
After the removal of the Bloodhound squadron, the RAF continued to use a small site near to the main entrance, utilising the 617 Sqn T2 hangar and other ancillary buildings as an engine maintenance and testing facility. This too has since closed and the main use is now as a quarry.
A long and distinguished life, Woodhall Spa’s operational losses totalled 91 aircraft, of which 74 were Lancasters and 17 Mosquitoes. Daring and brave crews, they gave their all for freedom and the love of flying.
Today little exists of this former airfield. Being a quarry and partly MOD, much of the land it is not accessible to the general public. Most of the buildings have long since gone and the runways mostly dug up. A few minor concrete ‘side roads’ are in situ and with searching some evidence can be found. The tower was demolished just after the war as were many of the other buildings and huts. Steps have now been taken to turn whats left into a nature reserve (see post dated 4th July 2015) and a memorial has been placed at the intersection of the runway remains. The best remnants can be seen a little way to the south-east at the former No 1 communal site at Thorpe Camp (see below).
A small number of buildings remain here utilised now as a museum. These include a war-time NAAFI able to accommodate 469 airmen and 71 officers, the ablutions block, ration store and various Nissen huts. A bomb shelter is also here, now flooded and blocked off along with other part brick structures.
In the adjacent woods, the airmen’s quarters and other buildings can be found, now derelict and in a dangerous condition. Odd buildings are scattered about the various sites but these too are few and far between.
Considering the history of Woodhall Spa, the men who flew from here, the operations they undertook, the testing of revolutionary equipment, the new and deadly bombs, it has suffered possibly greater than most and much of this history, if it were not for the Thorpe Camp museum, would now be lost forever. Now it has become a nature reserve in part, then maybe, just maybe, the footsteps of those who were stationed here may once again be walked by others and their memories brought back to life.
Thorpe Camp Museum
Thorpe camp museum *2 sits on the original communal site 1 on the former RAF Woodhall Spa and was acquired in 1988 by a group of volunteers (The Thorpe Camp Preservation Group) who have utilised the original buildings and pathways that would have been used by RAF personnel during their stay at Woodhall Spa. Entrance is a nominal fee and worth every penny.
A number of original huts and buildings display a range of letters, photos, memorabilia and other artefacts that take you through aspects of life both at Woodhall Spa and Lincolnshire life during the Second World War. Specific displays tell you about each of the four squadrons based here (97, 617, 619 (Dambusters) and 627) , the crew members, aircraft and personal stories. A memorial stands at the centre of the site reflecting their dedication.
Extensive work has been done to research the famous dams raid of 617 Squadron, how the bouncing bomb was developed, how it worked and what the aftermath of the operation was.
A small shop provides food and drink, and is a welcome break after a long journey.
A civilian section shows life ‘at home’. Weddings of the Second World War were scant affairs due to lack of money and rationing, but brides made the most of what they had; examples of these are nicely displayed. The home guard, ARPs, and domestic life are all represented in this atmospheric museum.
Many young men were sent from within the borders of Lincolnshire on major operations such as ‘Market Garden‘, these too are represented through displays of uniforms, photos, letters and official documents.
Further buildings, also originals, house well stocked displays of the V1 and V2 development. The terror weapons used by Hitler to break the morale of the British people. Over 3000 of these V2s were used against targets in the UK predominately London and the South East. Models, photographs and documents again show the extent of this development.
Something I had never come across before was the idea of using arrester gear on heavy bombers where runways may have been shorter than ideal. The principle, based upon that used by the navy on their aircraft carriers, was to place one or more steel cables across the runway for a landing bomber to ‘catch’ as it landed. A small number of airfields in the UK has these, Woodhall Spa being one of them, and an original winch has been removed from the airfield and carefully refurbished. This now has pride of place in the museum. It is believed a further example remains on the airfield alongside the remains of the runway. A rather ingenious but ineffective idea, it was not widely used due to mislandings and the increased weight that the arrested gear added to an already heavy aircraft.
Thorpe Camp provides a chance to see inside a Lancaster cockpit. A replica, painstakingly built includes all the detail of an original Lancaster bomber. Other parts, including turrets, dials and engines can also be found in this dedicated exhibition room.
Staff at Woodhall Spa are carrying out renovation projects and have their own workshop to do this. The process can be viewed and makes for an added interest to the visit.
As an aviation enthusiast the trip is topped off with another feature in the form of a BAC Lightning F1A (XM192) in 111 Squadron markings standing proud beside another cold war relic the Bristol Bloodhound missile.
Using a range of original documents, photographs, letters and memorabilia, Thorpe Camp at Woodhall Spa is a delight to wander and a real insight not only into the life of this Second World War airfield but life during those hard times in general.
On leaving here, driving toward Woodhall Spa village, you used to pass a two-seat hunter on the right*3. Bought by a farmer for a restoration project, it was sadly left to deteriorate in the open. Many parts were missing and / or damaged. Research has shown that it is in fact made up of two Hunters joined together and not an original.
As you enter the village of Woodhall Spa, you are greeted by the ‘best towns’ award. A beautiful little village with a crossroad at the heart. Adjacent to this is a small car park and the famous Dambuster’s memorial, depicting a breached dam.
The names of the crew adorn the side, reminding us of those brave men who sacrificed themselves for this controversial raid. Whatever you think, it is a moving piece and you cannot but stand in silence contemplating it’s significance. A further memorial has since been added in this small park, specifically for 617 Sqn, including references to post WWII operations.
This For those requiring a small break, there is a cake shop in the village “Janet’s” which sells a good cup of tea and refreshments. “Janet’s” is full of RAF memorabilia, every inch of the wall is covered – a fascinating place to sit. Further up the road away from the memorial, you pass a long leafy road with a sports centre on your left. On your right after the woods, is the sign for Petwood Hotel. A formidable building, used by Guy Gibson and his crews as a mess hall whilst based at the nearby airfield. In the Squadron bar, are pictures and memorabilia of those times, which you can look at whist having your afternoon tea. One notable artefact above the bar is the large branch of a tree that was struck by a low flying Lancaster, punching its way through the Plexiglass bomb aimer’s window. The hotel allows you to wander at will through the old bars taking in the amazing history of the place.

The Petwood Hotel hosts many activities relating to the 1940s, housing memorabilia of 617 squadron and was home to the officers of the Dambusters. A fabulous place for afternoon tea too.
On leaving Woodhall Spa, turn east toward the old airfield of RAF East Kirkby, or west to the former RAF Metheringham. Today we go east first of all and to the former RAF Easy Kirkby before turning back on ourselves and RAF Metheringham.
RAF East Kirkby
RAF East Kirkby is one of many Bomber Command airfields located in the Eastern county of Lincolnshire, a region that known as ‘Bomber County’. During its life it was home to two main front line squadrons along with a handful of other support units.
The airfield sits some 4 miles south-west of Spilsby and 12 miles north of Boston, in an area strongly associated with the Romans. Indeed, Lincoln – or Lindum Colonia as the Romans called it – became one of the largest and most influential Roman towns in England. Later, this area was where many invading Vikings settled, providing the local towns with examples of their own Nordic names, many of which can still be seen today. As time passed, both the Normans and the armies of Cromwell played their own part in the development of Lincolnshire, meaning the region has been left littered with several hundred monuments and numerous sites of archaeological and historical interest to offer the visitor.
Being in the lower regions of Lincolnshire, parts of it are only 40 feet above sea level meaning it is an area with a rich agricultural history as well; some areas being used to grow crops and of course tulips, bringing a wealth of colour and a wide range of crop to the area. It is all this that gives Lincolnshire both its beauty and its wide ranging historical interest.
Initially, East Kirkby airfield was built as a decoy site for nearby Coningsby and Manby, the site, complete with decoy wooden Whitley bombers, was decommissioned on June 27th 1941 and the area designated for a class A airfield – RAF East Kirkby. Following requisition of the farmland in 1942, construction began by the building company John Laing & Sons Ltd., which included, amongst others, the first flushing toilets in the area. The airfield was finally completed in 1943, opening on August 20th that same year under the control of Bomber Command.
Located to the south-east of the village that gave it its name, the apex of the ‘A’, formed by the three standard runways, pointed westward with the main runway approximately north-south and the two subsidiaries west to north-east and west to south-east, each being the standard 2,000 and 1,400 yards in length and 50 yards wide.
As a bomber airfield the much needed runways would be of a concrete construction, and the airfield would boast six T2 hangars and a single B1 for maintenance and storage; a technical area stood to the north-west, with accommodation and the bomb store, spread around the area away from the main airfield site. Dispersals for aircraft storage and preparation consisted of twenty-seven spectacle hardstands along with five loop hardstands, all located around the extensive perimeter track.
As a decoy site, it had been bombed on several occasions, and having accommodation and high explosives near to the airfield was not a good combination. These accommodation blocks were of a ‘temporary’ construction, very different to the luxury of Scampton, from where the first residents would come. At its height RAF East Kirkby could cater for 1,965 RAF personnel with a further 482 WAAFs all of mixed rank.
Initial ownership went to 5 Group Bomber Command, whose headquarters were at the time at Morton Hall near Swinderby, in the North Kesteven district of Lincolnshire, and would operate as 55 Base, the parent station of sub-stations Spilsby and Strubby.

A somewhat posed photo of Flt. Sgt. J Morgan, the rear gunner of a 630 Sqn. Lancaster at East Kirkby. @IWM (CH 12776)
The first resident unit was that of 57 Squadron who took it on immediately upon its opening, bringing both the Lancaster MK.I and MK.III with them.
After forming in 1916, they were, like many other squadrons at that time, disbanded after the war’s end in 1919, but then, as similar events unfolded on the continent once more, they were reformed (in 1931) to run continuously to the end of the Second World War. With further breaks post-war, they would continue to operate up to the current day, flying a wide range of aircraft from Victor tankers in the Falklands to their current model the Prefect T1 trainer at RAF Cranwell.
57’s history goes far deeper than that though, for it was whilst at Scampton, their previous home before East Kirkby, that ‘C’ Flight was separated from the main squadron to form the basis of 617 Squadron, better known as ‘The Dambusters‘; the Flight Commander, Sqn. Ldr. ‘Dinghy’ Young only being appointed to 57 Sqn a matter of weeks before the transfer took place.
However, it was at East Kirkby that 57 Squadron were now based. On August 27th 1943, just after the split, the advanced party arrived at East Kirkby to start what would be three days of moving and settling in. The first section of the main party arrived on the 28th with the remainder joining them on the 29th. During this time all flying operations were understandably cancelled and the time was allocated to the huge task of moving men and equipment over to their new base.
Operations commenced quickly on the 30th, when fourteen aircraft were detailed for operations to Munchen-Gladbach. All aircraft except one, completed the operation in which ground defences were ‘light’ and bombing was recorded as being ‘good’ with a large explosion seen in the target area. The only casualty of the flight being Lancaster MK.III ‘ED655’ which returned early with an engine failure. Thankfully though, there were no injuries nor any further problems incurred.
On the following night another fourteen aircraft were detailed to attack Berlin, the ‘big city’, an operation which brought August to an end and a total of twelve operations (179 sorties) amounting to over 940 hours flying time for the month.
It wouldn’t be long though before the first causalities would arise at the new station. On the night of September 3rd 1943, Lancaster ‘JA914’ DX-O was part of another fourteen flight raid on Berlin. On board that night was Australian Pilot Flt. Sgt. W. Grindley and his crew, which included one other Australian and a New Zealander.
After departing East Kirkby at 19:30 hrs, the aircraft made its way toward the capital. As it neared the target, search lights managed to cone the bomber, allowing a German night fighter (FW190) flown by pilot Unteroffizier Fritz Brinkmann of the Stab/JG 300, to attack the aircraft, bringing it down at Zehrensdorf with the loss of all seven crewmen on board.
Three of the crew were recovered and remained buried in the Berlin 1939-1945 War Cemetery whilst the remaining four were not. They have been commemorated on the Runnymede Memorial. The remains of the bomber were themselves discovered in a lake, and recovered on September 29th 1997; a large section of wing which is now displayed in the Deutsches Technik Museum, in Berlin.*1
On the 22nd September, a further crew were lost when an intruder, since known to be Major Wolf Dietrich Meister of the Stab V./KG 2, flying an Me 410 A-1 from Schiphol airfield, followed the bomber home and intercepted it near to the airfield. As it fell from the sky both the Flight Engineer and the Bomb Aimer managed to escape the burning wreck, both parachuting to safety, but the other five failed to get out and were killed in the resultant crash and fire.
The opening of September was however, the tip of the iceberg, for on the night of 23rd – 24th, three more aircraft were lost whilst on operations to Mannheim; all but five of the twenty-one men involved being killed, with those surviving five being incarcerated by the German forces. The operation had seen almost 630 aircraft take part in a raid that resulted in huge devastation with over 25,000 people being bombed out of their homes.
With the loss of two further aircraft in the closing days of September, the total dead or captured stood at seven Lancasters (forty-nine crewmen) with only four airmen returning to their Lincolnshire home. It had been a devastating start for the squadron at their new home in Lincolnshire.
October 1943 was much the same, major battles over the German Reich took further tolls with another four Lancasters falling from the skies. Most of these crews were also killed with just a handful surviving to be taken prisoner. The numbers of experienced crews on roll were quickly dwindling and replacements were now urgently needed.

The Lancaster ‘DX-F’ at East Kirkby, paying tribute to all those who flew from the airfield and in Bomber Command.
Then in mid November, 57 Sqn would be split for a second time to form yet another new squadron. This time, ‘B’ Flight were taken out and re-designated 630 Sqn. Initially being given the designation of an auxiliary squadron, it was however, a status that was never achieved. The entire flight consisting of nine crews and 106 ground staff, were led by the American, Sqn. Ldr. Malcom Crocker DFC, who simply moved across the airfield locating to new quarters and new dispersals, thus creating two operational squadrons at the site. Being battle hardened already, it took less than three days to complete the move before operations for them began once again.
November also saw Bomber Command enter its fourth month of the ‘Battle of Berlin‘, a period that saw intense bombing of the German capital with repeated raids on the city by heavy bombers of the RAF. It was also a time when the ill-fated Stirlings were finally pulled out of front line bombing campaigns, their losses becoming insurmountable. The decision to do so however, would put further pressure on the Lancaster and Halifax crews who were then left to complete the job with fewer aircraft and increasingly tired crews.
This period would become one of the RAF’s most testing times, and for the next four and a half months, Bomber Command, led by Sir Arthur Harris, would continue to pound Berlin and other major cities deep inside Germany. The winter would be harsh, flights would be long, and it would be a gruelling time for the crews of Bomber Command.
The void left by the Stirlings was filled by the Halifaxes, and their loses now also soared. The battle for Berlin was a battle that would quickly diminish the capability of the RAF if loses were to continue at their current pace.
As the war entered 1944, the crews of Bomber Command became weakened and tired. Extensive battles had taken their toll and a rest was much needed. With poor weather dominating January that rest came, as crews were grounded unable to fly in the appalling winter weather.
The new year would see 617 Squadron dominate the way for 5 Group, their fame and successes taking a large chunk of the new reels. However, at East Kirkby, 630 Squadron would take on a new commander with the arrival of Wing Commander Deas in early February, taking over from Wing Commander J. Rollinson. Deas would continue to lead the squadron for the next five months, as it battled its way through the harsh winter period into spring and onto summer.
The pressure was however on Harris. He was now ordered to turn his men away from Berlin and help the Americans with the invasion plans supporting them in Operation Argument, otherwise known as ‘Big Week’. The operation was designed to weaken the German aircraft industry to prevent reinforcements of aircraft in the build up and launch of Operation Overlord.
In one last vain attempt to hit the capital, Harris planned four nights of raids in February, but poor weather curtailed these allowing only one raid to take place that on the night of the 15th – 16th February.
In the raid, which proved to be Bomber Command’s penultimate flight over the city, both 57 and 630 Squadrons would be involved. A mix of almost 900 Halifaxes and Lancasters saw losses amounting to over forty aircraft, one of these coming from 57 Sqn and another from 630 Sqn with the loss of all crewmen.
In order to lower losses, the formations would be concentrated, dropping 2,600 tonnes of bombs in just twenty minutes, a rain-storm of explosives that would see forty-five aircraft bomb every minute.*2
With that the Battle of Berlin came to an end, fizzling out as operations turned to The Rhine and its heavily defended industrial infrastructure.
The first area targeted was Leipzig, on the night of February 19th-20th. Here another 800 plus aircraft flew to Germany and back. They met determined German fighters as soon as they crossed the coast after which ensued a relentless air battle all the way to the target. Once there, it was completely covered in cloud and sky marking by the Pathfinders was the only possible method of identifying the target. In the operation, 630 Sqn put up nineteen aircraft and 57 Sqn, twenty; all but three returned home that night.
The Leipzig attack would prove to be a disaster for Bomber Command, strong winds meaning some bombers had arrived before the Pathfinders, and then had to circle the target for some considerable time before the markers arrived. This resulted in many of them being shot down by flak with some colliding in the dark, night sky. A loss of seventy-five aircraft that night led to the withdrawal of the second of the heavies – the Merlin powered Halifaxes – from front line operations; like the Stirlings before them, their loses had become unsustainable. This move put yet another heavy burden on the Lancasters crews, as it became the main heavy bomber now able to carry the war into Germany,
The night also proved to be an important one for one East Kirkby Pilot, W.O. J. White, whose determination to get the ‘job done’ and come home, led to him receiving the award of a DFM. In the attack, his rear gunner was mortally wounded, and the aircraft badly shot up with both hydraulics and an outer engine rendered unserviceable. Undeterred, W.O. White carried on to the target, dropping the bombs and then returning to England. On arrival, he managed to negotiate landing the crippled aircraft at an unfamiliar airfield away from home. His courage and determination being more than worthy of the award he received for his actions.
With no break nor time to rest, another operation was ordered the following night, and although the 20th-21st attack on Stuttgart was a clear scoreboard for 57 Sqn, 630 lost another two; one of these ‘ND563’ swinging violently to port after travelling three-quarters of the way along the main runway. After crashing through a boundary fence and crossing a road on its belly, the bomb load exploded before anyone could escape. It was a tragic loss of life for those based at East Kirkby.

BBC war correspondent Richard North interviews the crew of Lancaster “S -Sugar” of No. 630 Squadron RAF on their return to East Kirkby, after bombing the marshalling yards at Juvisy-sur-Orge, France. IWM (CH 12778)
February closed with operations to Schweinfurt and Augsburg, an enquiry into the crash of ND5663 and the funerals of those who had lost their lives that day. With one squadron each losing a further crew, losses were continuing to mount for the two squadrons.
The early spring months would finally draw to a close over two disastrous nights. The first, on 24th – 25th March, saw Harris send his men back to Berlin one more time. In a last effort to bomb the capital, the RAF sent another 800 plus aircraft to the German capital, it would prove to be one of the worst for 630 Sqn, when three aircraft, including that of W.O. J. White who had just been awarded the DFM, were lost.
It was a dramatic figure that would be repeated on the last night of the month, when almost another 800 aircraft made up of Lancasters, Halifaxes and Mosquitoes were sent to Nuremberg. Weather reports from a Meteorological Mosquito were ignored and whist the operation should have been cancelled, it went ahead. In a moon-filled sky, the result was carnage.
By the time all aircraft had returned, losses stood at 95 crews, almost 12% of the entire force sent out, and the biggest loss for the Command of the war so far. The weather experienced had caused the biggest problems, not only for the main bomber-stream, but also for the Pathfinders, with strong winds blowing many aircraft widely off track causing them to bomb Schweinfurt, some 50 miles away, by mistake. Of those that did bomb the correct target, many reported that they were unable to see it due to heavy cloud, which combined with the strong winds, forced both them and the Pathfinders to mark and bomb the wrong area. As a result, little damage was done to the city, and dropping bombs too early, caused ‘creep back’ to extend for some 10 miles ahead of the target. All-in-all more crews were lost that night then there were casualties on the ground, losses that were totally unsustainable for the command.
The German defences on both nights had been extensive and determined. Tame Boar and Wild Boar tactics along with Schrage Musik, the upward firing cannons, had devastated formations who were scattered far and wide. Harris had gambled with his crews and lost.
The disastrous nights of Berlin and Nuremberg led to a short pause in operations in much the same way as the dreaded raid on Schweinfurt did for the Americans. A new focus would take no chances, and precise bombing became the order of the day.
With spring at an end, thoughts turned back to the impending invasion and the bombing of pinpoint targets in France: Railways, munitions factories, troop concentrations and transport links became the focus for Harris’s Air Force. Throughout the month of April both East Kirkby squadrons were in operations, and whilst not significantly high, a number of aircraft were lost adding to the lengthening list of casualties and those now missing.
The end of this period of the war was remarkable for several reasons, notably when Wing Commander Leonard Cheshire of 617 Sqn, flew a Mosquito at low level and marked the target, a factory in Toulouse, with great success. This delighted Harris, who gave the all clear to 5 Group to operate independently of the Pathfinders of 8 Group, a decision that did little to heal the growing rift between Don Bennett and Ralph Cochrane who had taken the idea to Harris in the first place.
Other targets then became the focus for 5 Group including the railway yards at La Chapelle. In the operation Cheshire put this method to the test once more. with 617 Sqn again to marking the target in conjunction with 8 Group’s Pathfinders. In the operation, 247 Lancasters from 5 Group were ordered to attack a pin point target. In the attack, 57 Sqn lost two aircraft. Of these two Lancasters the first, LL893 ‘DX-J’ was lost with all seven lives over St-Omer whilst the second, Lancaster MK. III ND582 ‘DX-S’ crashed after attempting a landing at Croydon. After overshooting the runway the aircraft, piloted by Canadian F.O. H. Young, struck at least three homes in Lavender Vale, a street adjoining the airfield. Three of the crew died immediately and a further one died from his injuries in hospital.

Operation POINTBLANK. Groundsmen refuel Lancaster ND560 ‘DX-N’, 57 Squadron in preparation for a night attack on the railway yards at La Chapelle, France. IWM (CH 12868)
Summer then dawned, and overnight, May 22nd-23rd, Cheshire once more, put his method to the test. 617 Sqn were again to mark the target, but a heavily defended Brunswick led to heavy losses for both the East Kirkby squadrons, 57 losing three Lancaster Mk.IIIs and 630 Sqn another two. Only five airmen made it out alive, each one being captured by the German ground forces and so becoming prisoners of war.
These losses were however a mere pin-prick compared to June. The mission of 21st-22nd to Wesseling near Cologne proved to be yet another massacre for 5 Group who sent a total of 133 Lancasters to attack the city’s oil facilities. A number of squadrons took heavy loses including both East Kirkby’s 57 and 630 Sqns with six and five losses respectively. One of these aircraft was abandoned whilst another ditched in the sea allowing all crewmen to be rescued, but the overall loss proved to be devastating.
The spring – summer of 1944 was defining, not only had 5 Group shown that low-level marking could be done, but the attacks on targets in France meant that the Luftwaffe were at a disadvantage. Their night tactics, relying on long range bomber flights, could not manage with the shorter ‘quick’ attacks, and so losses from Bomber Command began to lessen.
This reduction allowed for restaffing, with a large number of officers, NCOs and airmen being both posted in and out of the two squadrons. It also allowed for training flights to take place, some 476 hours of operations compared to 729 hours for non-operational flights for 630 Sqn alone.
Like many places across the UK, the coming of D-Day, and the fragile success of the invasion led to an increase in morale at the station. Ground crews being acknowledged for their long hours and hard work in keeping aircraft flying and operationally ready, without them, these operations could not have taken place at all.
This extra effort and improved state continued for several months, and by August, it was acknowledged that morale had lifted, discipline was at a high and health was overall very good. Casualties were also down, a real boost considering the extra effort and number of operations that had been taking place over the last few months. The summer was at last ending on a high.
August’s improvement coincided with the liberation of Paris, a major landmark in the war’s progress. Ground forces were charging ahead. In the air, Bomber Command had played a small part in the offensive supporting ground troops as needed and now they were released from the tight grip SHAEF had held over them. Discussions followed as to where best place their bombs, oil and communication were one option or alternatively, a return to the bombing of the cities and morale busting; oil won over, and so, much to Harris’s disappointment, the bombing of oil based targets began.
The looseness of the criteria however, allowed Harris to circumnavigate the ‘rules’ and turn his attention to cities with an oil link. He had got his way and the Air Ministry had got theirs.
Although individual operation losses were relatively low, 57 Sqn tallied some 56 aircraft by the end of 1944, whilst 630 Sqn reached 57. Non-operational loses for the two units were also on an equal par.
On the penultimate day of the year, East Kirkby was to witness, a short distance away from the airfield, the crash of a B-17 attempting to land. Aircraft #42-97479 (UX-L) of the 327thBS 92nd BG based at Podington (Station 109), crashed in a field between the two small hamlets of Old Bolinbroke and Hareby. On board that day were nine crew men: 2nd Lt. Joseph Martin Van Stratton (Pilot); 2nd Lt. Edward A Porter (Co-pilot); Sgt. Charles H Chambers (Bombardier); 2nd Lt. John E Cowan (Navigator); Sgt. Arthur R Estrada (Radio Operator); Sgt. Harold Raymond Barner (Ball Turret Gunner); Sgt. Wilfred A Bedard (Wasit Gunner); Sgt. Thomas G Standish ((Top Turret Gunner) and Sgt. William D White (Tail Gunner), who all lost their lives.
The aircraft, a Lockheed/Vega B-17G-15-VE Flying Fortress named “Belle of Liberty“, had returned from operations to the Bullay railway bridge located south-west of Koblenz, in Germany. After suffering engine failure, the pilot decided to abort the mission and attempt a landing at East Kirkby. In poor visibility and with one engine out, he overshot the runway and pulled up to attempt a second try. A second propeller then began windmilling and in trying to gain height to avoid a hill, the B-17 stalled and crashed.
A small memorial plaque has since been laid at the site in commemoration of those lost.
The winter of 1944-45 was one of the worst, ground troops were by now entrenched in the Ardennes around Bastogne, with the German army preparing for one last push through the forests. Fog and snow kept many airfields non-operational in the UK, aircraft struggling to get much needed support across to the continent.
At East Kirkby, January started on high spirits, but on the 9th, 630 Sqn Lancaster PD317 ‘LE-G’ struggled to get airborne when one of its engines cut out on take off. After jettisoning its bombs, the pilot, F.O. G Billings, opened the throttle to attempt a circuit and landing. However, the port wing lost lift and dropped causing the aircraft to cartwheel injuring five airmen and killing two. With one further loss on the 14th, this brought the spring tally to two aircraft. However, good news did soon come as six of the seven crew were repatriated by the April. The seventh airmen, W.O. E Edwards, struck the tail plane on baling out and died the next day.
Otherwise, 57 Sqn, scraped through with a clean sheet and no operational losses were encountered, but they did suffer an unfortunate incident when ‘DX-N’ PB382 (the predecessor of DX-N below) entered Swedish airspace and was shot down by flak on the night of February 8th-9th.
The losses encountered by 57 and 630 Sqn, were only pipped by the tragic accident that was reported to have happened on the 17th of April. Although the operational records record no evidence of the accident, even to the point of showing some of the aircraft involved taking part and completing their operations, it is recorded in some resources that six Lancasters of 57 Squadron were destroyed following a fire in the fuselage of Lancaster PB360. As a result of the fire, four men were killed and a further five injured, along with several civilian workers near the site.
The fire started at 17:45, causing a series of explosions which destroyed the five other Lancasters parked nearby. The Hangar on the airfield was also badly damaged, as was a neighbouring farm. The fires were so severe that fire crews were brought in from nearby airfields and the area was not declared ‘safe’ until the following day. The Lancasters involved were: PB360 (MK.III) ‘DX-N’; ND472 (MK.III) ‘DX-I’; LM673 (MK.III) ‘DX-U’; RF195 (MK.I) ‘DX-‘; PD347 (MK.I) ‘DX-P’ and NN765 (MK.I) ‘DX-‘.*3
By now German resistance was minimal. Fighters were rarely encountered in any number and flak batteries were reducing in their accuracy and intensity. By May, the war was at and end, and quickly both ‘Exodus’ and training flights became the norm along with cross country and high level bombing training flights taking the front stage. For 630 Sqn July signified the end, after a period of intense recruiting the squadron was disbanded after serving for approximately eighteen months of the war.
During that time they had shown great courage in action. On average they had flown 1,087 hours of operational flying per month and 286 hours on non-operational flights. This amounted to 2,147 operations over enemy territory during which 64 aircraft had been lost. With another six crashing, the toll was high, and their medal tally reflected that, with in excess of 60 awards being granted.
In a last days before disbandment a sports challenge with 57 Squadron allowed 630 to show their colours one last time, winning the overall trophy, and with a party to celebrate that night, the squadron went out on a high. The final day saw the last parade and the handing over of the squadron crest to the Air Ministry for safe keeping. With that, 630 squadron disbanded.
Their place at East Kirkby didn’t stay vacant for long though, for on the 27th July, 460 Sqn arrived to join 57 Sqn and serve its lasts days here at this Lincolnshire airfield.
57 Sqn would continue on, taking on the Lincoln bomber in August as a replacement for the Lancaster although numbers remained low at this time. Fighter affiliation, high level bombing training and cross country flights became the main focus, along with ferrying flights into the European continent bringing back personnel and equipment; a schedule that continued for the next four months, its time finally being called on November 25th 1945.
Throughout the war 57 Sqn had served with distinction, providing crews for not just one but two different squadrons, one of which went on to become perhaps the most famous unit in the RAF’s history. It was a success however, that came at a cost, with the highest loss rate of the whole of Bomber Command, they had taken part in some of Europe’s most ferocious aerial battles and still went on to perform admirably.
On disbandment, 103 Squadron then at Elsham Woods, was immediately renumbered as 57 Sqn, and the unit number lived on. The majority of personnel from the original 57 Sqn were transferred to the RAF’s Holding Station RAF Blyton Holding Unit, along with personnel from several other serving squadrons. Seven three-men crews remained at East Kirkby to ferry the Lancasters away whilst six crews transferred to Scampton to form the basis of the new squadron along with three Lincoln bombers.
460 Sqn an Australian unit, had also served well during its war time life. Being originally formed on November 25th 1941, it was made up of Australian crews, flown Wellingtons, Halifaxes and then Lancaster I and IIIs. Its move to East Kirkby from Binbrook signifying its end, as training flights took over bombing missions and personnel began to be transferred out. By October it too had disbanded.
In an acknowledgement of their bravery, the closing remarks in the Operation Record Books state how the Australian had been warmly welcomed to our shores and how they had cemented a great bond between the two allies against a common enemy. Appreciation and thanks was warmly given to those who had served in the unit.
With the war’s end, East Kirkby was rundown, but between spring 1946 and February 1948, a detachment of Mosquito B.IVs from Coningsby’s 139 (Jamaica) Sqn, operated here, joined between August 1947 and February 1948 by 231 Operational Conversion Unit (OCU) also on detachment from Coningsby. Flying a mix of Airspeed Oxfords, Avro Ansons & de Havilland Mosquito B.IVs, they were the last RAF units to use the airfield before it entered care and maintenance.
Then in 1951, the US Strategic Command 3rd Air Force took over the site, intending to use it as a stand-by airfield. As part of the plan, the runway was extended by 1,230 yards along with an expansion to the apron. Both the 3931st ABG and 3917th ABS were based here but only visiting C-47 ‘Skytrains’ (a derivative of the Dakota) of the 7th Air Division’s Rescue Squadrons, ever arrived.
Eventually, on 31 October 1958, the airfield was returned to Air Ministry under ‘Big Shuffle’ , the reorganisation of the Air Force and its sites in the UK and Europe.*4
With that, East Kirkby closed for good, being sold off in 1964 when it turned once again to agriculture. However, bought by the Panton Brothers, it was turned into a living museum including a taxiable Lancaster to commemorate not only the third brother – Christopher Panton, who was killed on a bombing raid over Nuremberg on 30th – 31st March, 1944 – but all those who served in Bomber Command during World War II.
Part of the museum includes the chapel, a stained glass window and memorial board listing all those who died whilst serving at the airfield in both 57 and 630 Sqn, are poignant reminders of the toll on human life at this one small Lincolnshire airfield.
East Kirkby Heritage Centre.
As the Lincolnshire countryside unfolds before you, and you can just imagine (in-between the sounds of jet engine) the Merlins, rumbling above you. Here is a relatively little known airfield, where a real story has unfolded. A taxiable Lancaster ‘Just Jane’sits proudly in its hangar, next to a Dakota. Purchased by two brothers, ‘Just Jane’ regularly taxis carrying fare paying passengers around the airfield. The long-term project is to return her to flight giving two airworthy Lancasters in this country – what a sight to be hold. Around the aircraft are the stark reminders of the darker side of aviation. Bits taken from crashed aircraft along with photos, personal artefacts recovered from the sites, and a range of military vehicles all add to the historical content of the trip.
The museum*5 is very well laid out. A good, clear guide tells you about the history of the site, the individual buildings (which are superbly renovated) and all the displays which are housed in huts. It even points out the bullet hole in the flag pole from the marauding German night fighter. Many of the displays were new to me and a very pleasant surprise to see. The watch tower, one of the best preserved in this country, has mannequins, sounds and artefacts set out as it would have been when waiting for ‘the boys’ to return from one of their war-time sorties.
With many displays, open days and other events, it is well worth the visit.
On leaving East Kirkby head back on yourself to Woodhall Spa and continue on. The road take you to another of Bomber Command’s airfields, an airfield that lasted until the war’s end featuring only one major flying unit, 106 Squadron. Today, we visit the former base RAF Metheringham.
RAF Metheringham.
Located on the edge of the Lincolnshire Fens 3 miles east of the Lincoln Cliff escarpment, and near to the village from which it takes its name, Metheringham was opened in 1943 as a class ‘A’ bomber airfield under the control of No. 54 Base, 5 Group, RAF Bomber Command. It would fall under the control of the main base at RAF Coningsby, operating in conjunction with RAF Woodhall Spa, in a three station network implemented to streamline the Bomber Command structure.
Like many airfields of the time, it had the usual three concrete runways; a main runway running slightly off north-south at 2,000 yds, and two additional runways of 1,400 yds each running north-east to south-west and north-west to south-east. The technical area was located to the west of the airfield, with the huge bomb store to the north. Metheringham had two T2 hangars and one B1, along with numerous spectacle hardstands around the perimeter track.

Large sections of Metheringham’s runways still exist mainly as public highways. The line of trees denotes a further runway.
The accommodation areas, mainly Nissen hutting, were spread to the south and west of the airfield, separated from the main airfield by the public highway, a feature common with many late wartime airfields. The entire site covered 650 acres, previously utilised as forest or rich farmland,
Built from requisitioned land over the winter of 1942/43, construction was not complete until after the advanced party arrived in early November 1942. Described by some as ‘cold’, ‘bleak’ and ‘inhospitable’, it was not unlike the many other unfinished wartime airfields scattered across Britain at the time. Muddy and with little in the way of creature comforts, it was soon to be home for bomber crews of the Royal Air Force, who would reside here for the remainder of the war.
With the advanced party hurriedly connecting mains water and power, the first and primary unit to serve from the airfield, 106 Squadron, began arriving hoping for something more than cold huts and muddy pathways.
A First World War Squadron who had been disbanded in 1919 and reformed in 1938 as war loomed, 106 Squadron had initially operated single engined and twin-engined light trainers before transferring to No. 5 Group and bombers. It first real foray into the bomber war was with the under-powered Manchester before switching to the far superior big sister, the Lancaster, in May 1942. This change over occurred at their previous station RAF Syerston, and within a week of their November 11th arrival here at Metheringham, they were flying their first Metheringham mission, and it would be right into the German Heartland.
Following on from the usual familiarisation flights, thirteen Lancasters of 106 Sqn would take to the air on the night of November 18th/19th for a bombing raid on the German capital. Mid November signified the start of a period known as the ‘Battle of Berlin’, a period in the Second World War where Air Chief Marshal Sir Arthur Harris, would finally get the chance to put into practice the idea that massed bombing of the capital would bring about the demise of the morale of the population by sustained attacks from Bomber Command. After witnessing first hand the Blitz of Britain’s cities, Harris was determined that such a campaign could succeed. However, ignoring the fact that the German’s own example had failed in reducing the British morale, he pressed on, sending wave after wave of bombers deep into Germany and Berlin itself.
So it began on that November night. With each 106 Sqn Lancaster carrying a 4,000lb bomb along with a mix of smaller bombs, they set off for Berlin. With moderate flak over the target, and no night-fighters encountered, resultant damage was light especially compared to some missions that would be flown by the Command.
The raid itself was not considered a great success, and whilst no major injuries were sustained on the mission, Sgt. R. Smith, the Mid upper gunner of Lancaster JB642, suffered severe frost bite after passing out due to a faulty Oxygen system in the aircraft. After landing at the fighter airfield at RAF Tangmere, Sgt Smith was treated for his injuries.
With one other aircraft landing away from base, the remainder of 106 Sqn all made it back to Metheringham with relatively minor damage. A remarkable escape considering the nature of the target.
A return to Berlin saw 106 Sqn back in the air on the 22nd/23rd and then again on the following night 23rd/24th November. The continuing spell of good luck saw all crews return safely again with only light to moderate damage to their aircraft. However, the night of 26th/27th would see 106’s luck finally run out and the first Metheringham loss.
Lancasters JB592 piloted By F/O. J. Hoboken DFC (his third flight to the capital that week) and ED873 piloted by F/O. R. Neil, were both lost that night. JB592, was brought down not far from Gross-Karben, in Hesse Germany with the loss of all the crew on board. ED873 suffered early engine problems with the starboard outer engine surging not long after take off. Once passed the coast, the 4,000 lb bomb was safely jettisoned and sent to the waters below where it was seen to explode by the crew. The aircraft then turned to land, overshot the runway and crashed into a field opposite the airfield. The crew were uninjured apart from the rear gunner (Sgt. Parker) who received minor injuries in the crash. This injury would however, prove to be a godsend, playing a vital role in his survival later on. This third night of bombing saw a force of 443 Lancasters take a heavy toll, with 28 being lost in action over the continent and another 14 over England. A loss rate of over 6%.
It was F/O. Neil’s crew who, after their lucky escape, would fall as the next victims of Berlin’s defence. With the original rear gunner still out of action due to the broken arm received in the last crash, he was replaced by Sgt. G. Stubbs, who made his last and fatal flight in ED874 on the night of December 2nd/3rd. The aircraft was brought down with the loss of all those on board, including the replacement Sgt. Stubbs. Berlin was fast becoming a rather large and sharp thorn in the side of Metheringham crews who by now, longed for a change in the target.
With one more Lancaster lost that year (Lancaster MK.III ‘JB638’, ZN-G) again with all on board, the cold 1943 winter drew to a close with many empty bunks in the Metheringham huts. It would be a long and bitter winter though, a winter that would last for several months over the 1943/44 period and all as the Battle for Berlin continued to rage on.
The New Year 1944 should have brought new hope for the Metheringham crews, but sadly things were to be worse – much worse. In fact, it would go on to prove to be the worst year in 106 Sqn’s history with their highest losses experienced to date.
The year began with fine but cold weather recorded as fifteen crews reported for duty on New Years Day. With bated breath they waited for the curtain to be pulled back to see where the bomb run marker would now take them. A thin line that denoted high chances of survival or low. But once again, and to the dismay of crews, the flight line marked its way across the continent to Berlin, it would be yet another night over the capital. With a take off time of 23:59, crews were briefed, checks carried out and engines started. Over the target 10/10 cloud were reported, so bombing was carried out on Pathfinder markers, with many of the Metheringham aircraft verifying their position with H2S.
Although fifteen aircraft took off, only thirteen made it to Berlin, Lancasters JB642 ‘ZN-J’ and JB645 ‘ZN-F’, both MK.IIIs, were shot down with the loss of thirteen airmen. The youngest of these, Sergeant John Alfred Withington (s/n: 1628244) was only 18 years of age and one of the youngest causalities of Bomber Command. The only survivor, F/S. A. Elsworthy, was captured and taken to a POW camp, Stalag Luft III in the German province of Lower Silesia not far from the town of Sagan.
With yet more flights to Berlin, briefings were becoming rather repetitive, and January ended the way it began with the loss of another seven air crew led by RAAF pilot P/O. K Kirland. Over the whole month, 106 Squadron had flown 123 sorties over nine nights, a total of 769 flying hours, dropping 497 tons of bombs, the second highest total in the whole of No. 5 Group.
During the 1940s, fog was a particular problem around Britain’s airfields, often reducing visibility down to virtually nil, meaning bombers could neither take off nor land. Arthur Harris realising the effect this was having on his bomber operations, requested investigations be carried out into a possible method for clearing the fog thus allowing bombers to operate in this appalling conditions and widening the possibilities of operations in bad weather.
Churchill, influenced by Harris’s argument, instructed his Scientific Adviser Lord Cherwell to begin action at once, and so the Petroleum Warfare Department began to assemble a team of experts – who had already carried out some investigations into the weather and methods for dealing with fog – into a team to investigate the problem. A wide ranging group of scientists and industrialists carried out research concluding that heat was by far the best method for clearing fog over the low lying landscape.
The requirement put forward was to clear a standard Class A runway of at least 1,000 yards long and 50 yards wide, and an area up to 100 feet above the ground – a staggering 1.65m cubic yards of air. Further limitations were then put on the order restricting the placement of any obstacles likely to endanger an aircraft within 50 feet of the runway’s edge. A mammoth task but one which saw the development of the oil burning FIDO system.
The FIDO (Fog Investigation and Dispersal Operation) system was developed under the leadership a British Civil Engineer Arthur Clifford Hartley, CBE who worked with the Petroleum Warfare Department, and whose initial ideas involved using one of two streams of fuel; petroleum trialled at RAF Graveley, and Coke trialled at RAF Lakenheath. After initial (and rather crude) tests at both Moody Down (petroleum) and Staines (coke), petroleum was found to be the better of the two fuels, and henceforth, the Gravely model was used as a template for fourteen further sites of which Metheringham was one.
Installed at Metheringham during early 1944, it saw pipes laid alongside the runway which when lit, created an initial mass of smoke. Once the system had ‘warmed up’ the smoke dissipated and the fog began to ‘burn off’ as the immense heat from the burners created an up draft of warm air.
By the war’s end FIDO had been used across England to assist in the landing of almost 2,500 aircraft most of which would otherwise have not been able to land without great danger to the crews or ground staff; it had been one of the war’s greatest success stories and was sold as such to the wider public. So successful in its outcomes, FIDO was intended to be installed at London’s major airport Heathrow, after the war, but the cost of running each system was astronomical, burning some 6,000 – 7,000 gallons of fuel in four minutes – the time it took to clear the designated volume of air. It is estimated that during its wartime use, something like 30 million gallons of fuel were burnt and whilst the cost to the taxpayer was tremendous, it is thought to have saved the lives of over 10,000 airmen in the process.*1
Back in the air, the night of March 15th/16th saw split missions with one section going to Stuttgart and and a further six aircraft heading to the aero-engine factory at Woippy in France. These six made up a total formation of twenty-two Lancasters, a flight that included 617 Sqn aircraft. With promises of good weather over the Metz region, it came as a huge disappointment to find 10/10 cloud cover over the entire target. Even with the target being identified on the H2S screen and five marker flares being dropped, the leader announced the mission scrubbed and all aircraft were instructed to return to base taking their full complement of bombs with them. So strong were the crew feelings that 617 Sqn’s leader, Leonard Cheshire, seriously considered complaining! However, despite this, all aircraft returned including those of 106 Sqn to Metheringham with only minor flak damage to ND331.

Lancaster B Mark IIIs of No. 106 Squadron at Metheringham,heading to Frankfurt. The attack on 22/23 March 1944 caused extensive destruction to eastern, central and western districts of the city. © IWM (CH 12543)
With the next few missions passing without major incident, the night of March 30th, would deal a hefty blow to the crews of 106 Sqn.
With take off starting at 22:15, seventeen Lancasters would depart Metheringham heading for Nurumberg carrying a range of 4,000lb, 1,000lb, 500lb, 41lb and 30lb bombs. Over the target, skymarkers guided the bomb-aimers as cloud was reported as heavy as 10/10 again. Searchlights and flak were evident as were fighters which attacked and damaged Lancaster ND332 piloted by F/O. Penman. The Lancaster, which claimed two enemy aircraft damaged, returned to England putting down on Manston’s emergency runway. Both the rear and mid upper turrets were out of action, one of the engines caught fire, and on landing, the undercarriage collapsed due to the enemy action. luckily though, no crewmen were injured in the sustained attack that caused the Lancaster’s severe damage.
A further Lancaster had to return early, Lancaster JB567 after suffering the failure of the port inner engine landing back at Metheringham after two and half hours into the flight. Similarly it was an engine failure that also caused the early return of JB641 this time landing three hours after departure. Three of the seventeen Lancasters were already out of action.
Meanwhile on the continent, Lancaster ND585, was reported missing, later being found to have been shot down by a German night fighter, crashing in Belgium with the loss of all its crew. On board was, at 18 years old, another of Bomber Command’s youngest ever crewmen, Sgt. Julian Mackilligin RAFVR (S/N: 1804016), who even at his young age, was already half way through his operational quota. He was buried at the Hotton War Cemetery, Luxenbourg.
Next came another two losses, Lancasters JB566 piloted by F/S. T. Hall DFM and ND535 piloted by F/O. J Starkey. Both went down with the loss of all but four crewmen. The mission had indeed been costly, forty-two airmen were out of action, seventeen of them killed.*3
By the end of the first quarter of 1944, 106 Sqn had carried out more sorties than any other 5 Group squadron (358) losing 8 aircraft in the process. This gave the men of Metheringham an average of 19 sorties per aircraft in the first 90 days.
April began with a mix of bombing and ‘Gardening‘ missions, operations that included laying mines along the Koningberger Seekanel, with mines being dropped from as low as 150 ft. Even though some aircraft reported heavy ground fire from the banks of the Canal, the mission was deemed to be a great success and all aircraft returned safely.
The month continued to go well for the Metheringham crews, but the night of April 22nd / 23rd would take another toll on the morale of the crews. That night saw twenty Lancasters fly to Brunswick as part of a much larger force of 238 Lancasters and seventeen Mosquitoes. The mission, whilst generally uneventful, marked the first operation in low level target marking by No. 5 Group over a large city, an aid that proved fruitless on this occasion partly due to low cloud/haze obscuring the bomb aimer’s clear sight. With varying reports of cloud from 5/10 to no cloud and haze, all bombers reported bombing on markers, but damage and ground causalities were recorded as low.

The former Gymnasium now forms part of the museum and holds a range functions including weddings and talks.
RAF loses that night were also relatively low, with only four aircraft being lost from the whole flight. Sadly though, one of these, Lancaster MK.III ‘JB567’ ZN-E piloted by F/Lt. J. Lee was a Metheringham aircraft. F/Lt Lee had only one more mission to go before completing his first tour of duty. Only two of his crew survived, being picked up by German forces and sent to POW camps. This loss only went to strengthen the idea that it was difficult, if not impossible, to achieve a full tour of duty unscathed.
The next night 24th/25th April, 1944, took 106 Sqn back to Germany once more, to Munich and another ‘clear night’ with accurate bombing reported. But, then it was Schweinfurt a city that would become synonymous with high casualties especially amongst colleagues in the US Air Force.
Metheringham would send sixteen aircraft that night with take off commencing at 21.25 from the Lincolnshire airfield with another mix of 4,000lb, 41lb and 30lb bombs. Over the target, marking would again be low level by Mosquitoes but this time it was inaccurate. Strong winds hampered the bombers, with many of the bombs falling away from the main target. Crews reported large fires across the city accompanied by ‘large explosions’. Sadly these were not to be the target and as a result the mission was not deemed a success.
Of the 206 Lancasters sent out that night (26th/27th) twenty-one were lost to heavy and sustained night fighter attacks, a figure of 10% of the force, a terrible blow for Harris and his Command. From Metheringham, five aircraft failed to return, with a further one returning on three engines. Methringham’s loss that night was some 31%, a third of its force gone in one mission. It was a difficult mission for 106 Sqn, with thirty-six airmen lost, (JB601 was carrying a second pilot). Ten of these were taken alive as POWs, four managed to evade capture, whilst the rest were killed. The deaths of the remaining twenty-two must have had another huge impact in the Metheringham dining room that morning.
During this mission the remarkable actions by the crew of Lancaster ME669, and in particular Flight Engineer Sergeant Norman C. Jackson (later Warrant Officer), would become well known. After being hit several times by a night fighter, a fire started in the inner wing section next to the upper fuel tank. Sgt. Jackson, who had been wounded in the leg and shoulder, donned his parachute and grabbed a fire extinguisher before climbing out on to the wing through an escape hatch in the fuselage roof. Upon leaving, his parachute was deployed into the cockpit area, where his colleagues gathered it up and gradually fed the lines through the hole allowing Jackson to gain access to the fire in the wing. Undertaking such an act on a burning aircraft and at altitude, was no easy task and getting back, had he been successful, virtually impossible. The wind knocked the extinguisher out of his grip which prevented Jackson from succeeding in achieving his aim. The fire, now spreading, began to burn both his parachute, hands and face and fearing for his safety, his colleagues let go, releasing him from the stricken bomber. Sgt. Jackson fell to Earth, his parachute partially burned, opened and allowed him to reach the ground alive, but suffering several injuries in the process.
The 21 year old Canadian Captain, F/O. Frederick M. Miffin D.F.C., then ordered the crew to abandon the aircraft; himself and 20 year old F/Sgt, Norman H. Johnson (Air Gunner) both failing to survive.
Sgt. Jackson’s brave attempt to save his colleagues and their aircraft earned him the Victoria Cross for his actions, his citation being published in the Fourth Supplement to the London Gazette on Tuesday 23rd October 1945.*2
The Schweinfurt raid had been a major blow to the Metheringham crews, but it had also shown their courage and determination to win, regardless of the dangers to their own safety.
Another heavy blow on the night of 7th/8th May took another four aircraft along with all but one of the crew, Sgt. J Smith evading capture, in a month that would see a further six aircraft go down with heavy losses.
June 1944 would see another remarkable event take place. Although the entire crew of DV367 were lost on the night of 7th / 8th, they were all awarded the DFM for their action, an usual act in any squadron, and one that nonetheless reflected the bravery of RAF crews at that time.

Metheringham’s memorial garden rests besides a C-47 Dakota ‘KG651’ as a representative model that visited the airfield at the end of the war. Visitors are able to enter the aircraft and sit in the cockpit.
Following the Allied invasion of Normandy, the US forces would begin to use Metheringham as an evacuation point for wounded American troops from nearby Nocton Hall Military Hospital. Once a suitable recovery had been made, the troops were brought to Metheringham and flown on to Prestwick for onward travel and reparation to the United States.
Rarely a month would go by without the squadron facing some loss. Exactly a month later in July, Metheringham would see yet another dip in their crew numbers as five more aircraft went down on the mission to St.-Leu-D’Esserent – the flying bomb storage dump. A force of 208 Lancasters and thirteen Mosquitoes accurately bombed the mouth and access roads to the tunnels in which the bombs were being stored. Metheringham’s loss was particularly high, almost a third of the sixteen sent out being lost. Whilst many airmen were either captured or evaded capture, another eighteen were lost.
In September 1944, No. 1690 (Bomber) Defence Training Flight arrived ay Metheringham airfield. A unit formed seven months earlier at Syerston after 1485 (Bomber) Gunnery Flight was re-designated, it operated a number of single and twin engined aircraft including the Spitfire, Oxford and Wellington bomber under the code ‘9M’. They were used to train bomber crews in the art of defence against fighters, performing violent moves to throw off their attacker. One famous pilot of this unit who served at Metheringham was the Commanding Officer Sqn. Ldr. John Leslie Munro, CNZM, DSO, QSO, DFC, JP of 617 Sqn fame. The Flight would leave Metheringham in the summer of 1945, being disbanded in October that same year back at Syerston.
It had been a long and difficult war for the crews at RAF Metheringham. As the end of the war drew ever closer, they all knew their last mission would soon be here. On April 25th 1945, that day arrived.
Sixteen Lancasters took off to either bomb Tonsberg in the southern region of Norway, or mine the Oslo fjord. A last ditch effort to force the capitulation of the German leadership and end the conflict that had devastated the world for the last six years.
By the time the cease fire was announced, 106 squadron had flown 5,834 sorties with a loss of 187 aircraft (59 from Metheringham), 3.21% on average per mission. 17,781 tons of bombs and mines were dropped and 267 decorations awarded.
After the war, 106 Sqn was earmarked for ‘Tiger Force’ operations and training was tailored to meet these new requirements: fighter affiliation sorties, high level bombing and air-sea firing exercises. Also during May, operation ‘Exodus‘ was put into place and a number of 106 Sqn aircraft flew to the Continent to bring back POWs, many landing at Dunsfold on their return. On the 9th May, whilst evacuating POWs from Rheine airfield, one aircraft from 106 Sqn struck a bomb crater causing damage to the aircraft, the crew and their valuable cargo of POWs thankfully escaped unhurt. The aircraft was then repaired with parts being ferried over from Metheringham the next day. Between May 4th and May 11th, Metheringham crews repatriated 1,484 prisoners of war bringing them home from captivity.
During June aircraft were exchanged with those from 8 Group at RAF Oakington, RAF Warboys and RAF Graveley, allowing Operation ‘Firebrand‘ to be completed by the 19th. Other operations included ‘Rebecca‘, ‘Dodge‘, ‘Nickel‘ and ‘SPASM‘.
On June 15th, another Lancaster squadron, No. 467 (RAAF), joined 106 here at Metheringham. In the days preceding their arrival, they spent many hours dropping ordnance into the sea, a comment in the ORB stated “it seemed like the old days with all serviceable aircraft loaded with incendiaries and it looked like a real operational take off.” It goes on to say a ‘waste but necessary‘ reflecting perhaps the feelings of the men as the squadron wound down for the final few weeks.
The advanced party arrived to make sure the transition went smoothly, with the main party arriving shortly afterwards. Beer was supplied by Metheringham and the crews soon got to know each other well. On July 11th, an athletics competition was run between the two squadrons, involving contests such as ‘tug-o- war’, ‘hop, step and jump’, ‘throwing the cricket ball’ and distance races.
With the announcements of Japan’s capitulation on August 15th, all 106 Sqn ‘Tiger Force’ training flights were cancelled although it continued to be used as the basis of further training operations. B.A.B.S. (Beam Approach Beacon System) training also continued at the airfield.
Shortly after 467’s disbandment on September 30th 1945, October saw yet another Lancaster unit arrived at Metheringham, No. 189 Squadron who brought yet more Lancaster MK.Is and III. to be disposed of and they too were disbanded within a month.
The poor weather that had caused so many problems during the winters of the 1940s leading to Metheringham having FIDO installed, continued on into 1946 curtailing many flights and operations. On 13th February 1946 the final curtain came down and a memo came though to Metheringham to ‘stand down’ from all operational and non-operational flying as of 00:01, 15th February 1946. Sixteen aircraft were to be ferried to RAF Graveley to have Mark III H2S units fitted, although this was cancelled and the aircraft were sent to Waddington (10), Binbrook (1), Lindholme (4) and one further Lancaster going to Waddington. By 22nd February 1946 all aircraft had left Metheringham and the squadron no longer existed, 106 Squadron was once more consigned to the history books and Metheringham airfield would follow not long after. Men, machinery and administrative items were then disposed of in accordance with the relevant Bomber command instructions. By April, everyone had left, the site was stripped and placed in care and maintenance, a condition it remained in until December 1950, whereupon it was abandoned before being sold off ten years later.
Like many stations, local people used the accommodation sites for their own accommodation, the runways were eventually pulled up for hardcore, buildings and other metal structures were removed for scrap or sold off to farmers. By the early 1970s Metheringham had all but been wiped off the map. The Watch Office left to decay has since been bought by a local developer, with a mammoth task ahead of him he hopes to turn it into accommodation and a small museum/residential block.
Metheringham’s record of achievement was a proud one, with generally low loss statistics they were to face some of the toughest challenges of the war, losing many crews in the process. Their determination to survive and to win over the Nazi tyranny led to many brave and heroic acts, acts which helped secure the release of hundreds of captured airmen.
Metheringham’s gallant and brave young men, are all remembered in a small, but excellent museum that now utilises part of one of the accommodation areas. A memorial to the aircrew stands on the eastern perimeter track as a reminder of the 995 Airmen who were lost whilst serving with 106 Sqn.
Much of Metheringham’s runway and perimeter track still exists today, in most part as a public road. The width of the concrete bases far exceeding the width of the road. A memorial stands to the eastern side overlooking the main airfield site (Site 1) with lines of tress denoting the remainder of runways long gone. The main B1189 road dissects the accommodation areas with Site 1, as was common with late wartime airfields. The museum lies off the junction of this road and the main Woodhall Spa road B1191 along the entrance to Westmoor Farm. If taking the B1189 toward the Metheringham village, you will pass a number of former wartime buildings used as small industrial units and farm storage. These are on private land although the museum do organise visits to some of these at certain times of the year. After passing these, turn right, this road was one of the secondary runways and crosses the remains of the main runway part way down. It then bends to the right taking you along the perimeter track, and then right again to the memorial – a circular route that traverses what was the peri track. Several of the hardstands still survive, mainly on farm property and difficult to see from the ground, but the number of buildings still standing is quite remarkable for such a short lived airfield.
References and further reading (Woodhall Spa and Thorpe Camp).
*1 Author unknown, photo from the ‘Aircrew Remembered‘ website, August 2015
*2 The Thorpe Camp museum have a website. The museum was visited in July 2015 and this page has been updated since.
*3 The Hunter has since been sold/disposed of, and is no longer in the field (see comments section for details)
References and further reading (East Kirkby)
*1 Aviation Safety Network website accessed 19/10/24.
*2 Worrall, R., “Battle of Berlin 1943-44” Osprey Publishing. 2019.
*3 Chorley, W.R., “Bomber Command Losses pof the Second World War – Vol. 6 1945” Midland Counties Publications 1998.
*4 Francis. P & Crisp. G., “Military Command and Control Organisation Volume 4 – The United States Air Forces in the UK” on behalf of English Heritage.
*5 The East Kirkby Museum have a website which gives far more detail, opening times, and other other visitor information.
National archives: AIR 27/538/38; AIR 27/538/44; AIR 27/538/43; AIR 27/2152/8; AIR 27/2152/7; AIR 27/2152/29; AIR 27/540/13; AIR 27/540/21; AIR 27/1910/11; AIR 27/540/8; AIR 27/540/7
American Air Museum Website Accessed 20.10.24
International Bomber Command Centre has several personal stories on their website, and is well worth a read.
Lincolnshire Aviation Heritage Centre Website.
References and further reading (RAF Metheringham)
*1 Fleming, J., “The Callendar Effect: The Life and Work of Guy Stewart Callendar (1898-1964)“, 2007, The American Meteorological Society
*2 The London Gazette, 23rd October 1945.
*3 Operational Record Book March 1944 – IWM AIR-27-834-6
Operational Record Book January 1944 – IWM AIR 27/834/1
Operational Record Book November 1943 – IWM AIR 27/833/22
Operational Record Book April 1944 – IWM AIR 27/834/8
Operational Record Book – Squadron Number: 106 Summary of Events: Y – IWM AIR 27/835/9, (01 May 1945 – 28 February 1946)
467 RAAF (Royal Australian Air Force) Summary of Events: Y 01 May 1945 – 30 September 1945 – IWM AIR 27/1931/33
Middlebrook. M., Everitt. C., “The Bomber Command War Diaries.” 1996, Midland Publishing.
Records of a 1690 BDTF pilot can be read on the Website ‘A Pilot’s Story‘.
Metheringham Airfield Museum website holds details of opening times, admission fees and special events. An excellent little museum it is well worth a visit.






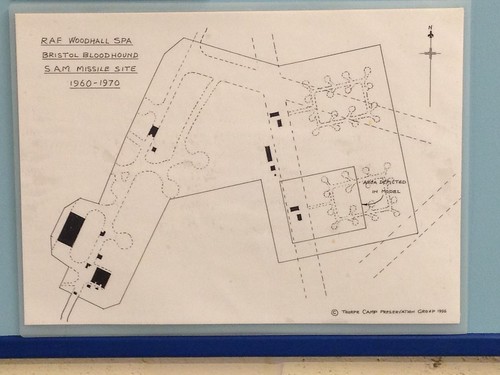














How have not put Raf Sutton Bridge on here for the lower Lincolnshire ones.
LikeLiked by 1 person
Hello Nicholas, Sutton Bridge is on a separate Trail ‘Gone but not forgotten’ each one completed as I do them. As a side, I have made a separate site for RAF Sutton Bridge as I’m researching it more deeply. If you have any knowledge or experience of it, I’d love to hear it.
LikeLike
on page 50-53 of Volume 1 of our books a story of East Kirkby and photo maintenance on the Dakota. One of the 172 places with Towers we visited.
http://www.controltowers.eu
LikeLiked by 1 person
Thanks.
LikeLike
Dear Andy, This has long been one of my most favourite trails of yours. You know why. It captured my imagination with its nostalgic trip back into the past, into the days of World War iI, where my heart has always been. Thank you for the journey. Since I read it so very many months ago, it has indeed been a journey. You are truly one of a kind. Keep up the excellent writing and the unparalleled personal touches that make the blog so special.
p.s. Don’t forget your promise of tea and cakes at the Petwood Hotel. I am still looking forward to it! Xxx
LikeLike
Thank you for your kind words, they were magical times and very hard for those who lived through them. I have learnt so much from these journeys, the people I have met and the research that has been carried out. Of course, the offer of tea and cake remains open whenever you can make it. x
LikeLike
Just to let you know, that the Hunter you talk of on the way into Woodhall Spa has now been sold and is no longer there.. All the best.. David.
LikeLike
Many thanks for commenting David. I was aware that since the visit it had been moved to somewhere else. But I wasn’t aware that is had been sold, hopefully to a good home for some TLC. Thanks again, please do let me know if you know where it went.
LikeLike